Cryptocurrencies have become increasingly popular in the UK, with more people and businesses investing in digital assets.
However, with the growth of the cryptocurrency market comes the risk of money laundering, terrorist financing, and other illicit activities. The risk and propensity for financial crime and fraudulent activity to occur is compounded by the fact that the crypto market in the UK is currently largely unregulated.
However, with Financial Action Task Force (FATF) guidance on cryptocurrency being issued as early as 2014, member nations have taken action to standardise AML requirements in the market in recent years as crypto gained popularity.
The British government is currently in a period of consultation to develop legislation which will regulate the sector in a way that is “consistent with its approach to traditional finance.” As part of these proposals, cryptocurrencies will be subject to the Financial Services and Markets Act 2000, under the remit of the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA).
Since January 2020, the FCA has been the supervisor of UK crypto asset businesses under the Money Laundering, Terrorist Financing and Transfer of Funds (Information on the Payer) Regulations 2017. Any crypto exchange operating in the UK has had to register with the FCA in order to operate.
While the FCA has oversight to check that crypto asset firms have effective anti-money laundering (AML) and terrorist financing procedures in place, the sector itself remains mostly unregulated.
It is estimated that 85% of current registration applications from crypto asset firms are rejected as companies fail to demonstrate sufficient AML procedures. In this article we explore four key factors to remember and share best practices for anti-money laundering compliance in the UK cryptocurrency market.
What are the AML risks associated with cryptocurrencies?
Virtual currencies such as Bitcoin and Ethereum developed at incredible speed, from unknown technology to an increasingly globally accepted payment method in a matter of years. As such, the unique and, in some cases, unfamiliar nature of crypto has left regulators and AML professionals with uncertainty around how to deal with these emerging payment methods. Policy responses are varied across the world: some embracing the new technology and opportunities that crypto poses, while others have completely limited its legitimate use entirely.
In June 2014, the FATF laid out four key AML/CFT risk factors presented by cryptoassets:
- the anonymity provided by the trade in virtual currencies on the internet
- the limited identification and verification of participants
- the lack of clarity regarding the responsibility for AML/CFT compliance, supervision and enforcement for these transactions that are segmented across several countries
- the lack of a central oversight body
These risks are still valid nearly a decade later, and awareness of these factors is critical in the fight against money laundering and financial crime in the crypto asset sector.
Establishing robust AML processes
As part of AML efforts, it is important to examine every risk associated with crypto assets and amend policies and processes accordingly in order to thwart illicit transactions that could be linked to money laundering and terrorist financing.
AML checks play an important role in satisfying the requirement of regulated businesses to undertake customer due diligence. These checks are about knowing your customer; verifying individuals are who they say they are, and ensuring a clear understanding of any risks associated with doing business with them.
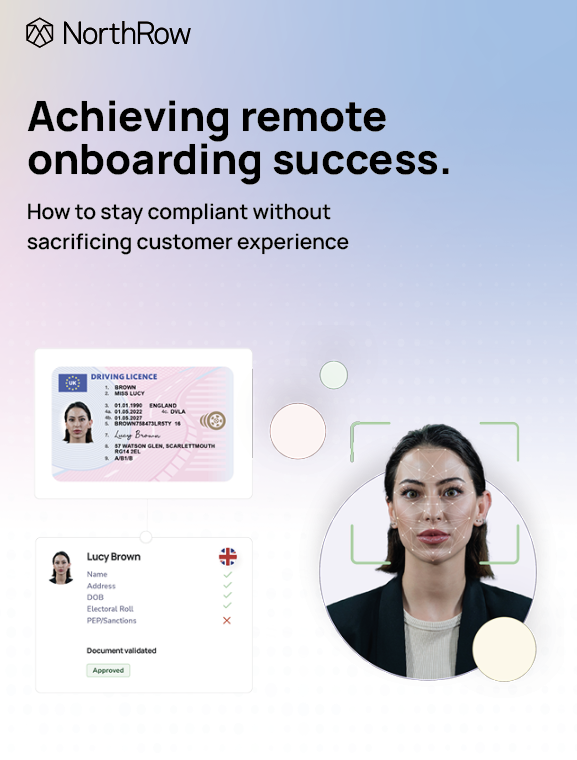
Comprehensive Know Your Customer (KYC) procedures
KYC procedures require cryptocurrency businesses to verify the identity of their customers, including their name, address, and date of birth. Often conducted at the beginning of a relationship when an individual may be making a purchase of crypto assets, businesses must ensure that they have adequate procedures in place to verify each customer’s identity, including scrutinising identity documents and confirming proof of address.
Ongoing Customer due diligence (CDD) and risk assessments
It is important for crypto firms to maintain confidence in the data collected as part of their KYC processes, making any changes and identifying any issues that may be suspicious, and may require further investigation.
The goal of CDD is to establish that any identified changes in status, behaviour and anything else relevant to your relationship with them, are innocent and relevant to their circumstances. Any changes are likely to be innocent (a name change through marriage for example), but they all need to be fact-checked to establish their veracity.
AML compliance is an ongoing process, and cryptocurrency businesses must conduct regular risk assessments and update policies and procedures to reflect any changes in the risk environment.
Reporting suspicious activity
Cryptocurrency businesses must report suspicious activity to the authorities. This includes suspicious transactions, attempted transactions, or any other activity that may be indicative of money laundering or terrorist financing. A company must implement suitable procedures for identifying and reporting suspicious activity, including training for staff and internal reporting protocols.
Cooperation with authorities
Cryptocurrency businesses must cooperate with the authorities and provide information when requested. Businesses must also ensure that they have procedures in place to respond to requests for information from the authorities, including audit trails, proof of due diligence and up-to-date record-keeping.
Using technology for AML compliance in crypto
As crypto assets become more and more popular, a growing compliance caseload can lead to bottlenecks in your KYC processes, and ultimately lead to a poor customer experience. Technology can deliver cryptocurrency firms with flexibility in their compliance and onboarding processes, and can lead to greater efficiency.
Here at NorthRow, our AML compliance software assigns every KYC case a simple ‘Yes’ or ‘No’ decision based upon your business’ pre-defined risk profile and requirements – without the need for manual intervention or further involvement.
Depending on your risk factors, our software can return an ‘auto-decision’ via a RAG system (Red, Amber, Green) to denote whether you can safely do business with a customer or not, or whether cases require further due diligence.
Our intuitive software can support the onboarding of new customers with comprehensive KYC checks that screen for PEPs, sanctions, legal events, adverse media and, where needed, remote digital ID verification can be undertaken including liveness detection, and address verification to ensure consumers are who they claim to be.
AML compliance is crucial for the UK cryptocurrency market to prevent criminal activity and protect investors. With modern technology, crypto businesses can make faster decisions and onboard customers in seconds, not days, so that they can continue to actively contribute to the ongoing growth and success of their business.